Mendel’s three laws pdf
Mendel’s three laws pdf
Gregor Johann Mendel was born on July 22, 1822 to peasant parents in a small agrarian town in Czechoslovakia. During his childhood he worked as a gardener, and as a young man attended the Olmutz Philosophical Institute.
12 Exceptions to Mendel’s Laws These laws are true for the genes Mendel observed, but exceptions to these laws in more experiments lead to many discoveries, including:
The principles that govern heredity were discovered by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1860s. One of these principles, now called Mendel’s Law of Segregation, states that allele pairs separate or segregate during gamete formation, and randomly unite at fertilization.
Independent assortment is a basic principle of genetics developed by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1860s. Mendel formulated this principle after discovering another principle known as Mendel’s law of segregation, both of which govern heredity.
17/05/2012 · In an attempt to explain experimental results and confirm Mendel’s laws, chromosomal crossover was formulated and described by Thomas Morgan (coincidentally, his student John Northrop was a teacher of botany at Hunter College, the author’s …
Or in 1900, when three botanists, Hugo de Vries in the Netherlands, Carl Correns in Germany, and Erich von Tschermak in Austria, independently rediscovered Mendel’s laws? Or in 1902 when Bateson’s book, A Defence of Mendel’s Principles of Heredity explicitly connected Mendel’s laws with the general question of ‘heredity’ [2] ?
Mendel’s Three Laws of Inheritance Mendel’s research produced three laws of inheritance that are true today. Summary of the Three Laws Law of Dominance (Dominate vs Recessive Alleles) In a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits, only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation. All offspring will be hybrid for a trait and will have only the dominant trait
Mendel through his extensive experimentation and analysis founded the three laws or principles of inheritance: The law of segregation, the law of dominance, and the law of independent assortment. He developed the concepts of dominant and recessive genes that explain how genetic traits are passed along from generation to generation.
Mendel’s Laws: Independent Assortment A scientist who achieves success using one particular technique always uses that technique in the initial phase of solving the next problem.
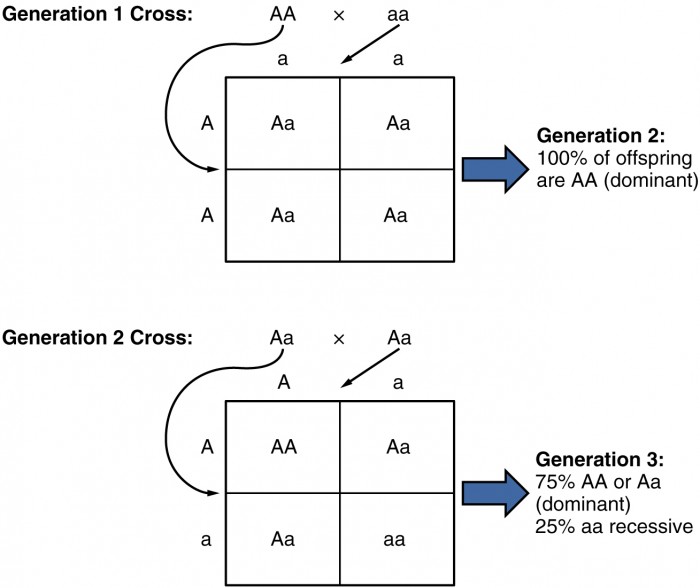
Mendel’s First Law: When a plant with two dominant (DD) alleles is crossed with a plant having two recessive (rr) alleles (top row), the first generation of plants (middle row) will all have one dominant and one recessive (Dr) allele.
Abstract. For more than 150 years now the enigma of the disregard of the basic laws of heredity detected by Mendel in the 1860s for at least 34 years (from 1865 to 1900) has inspired a large number of conjectures and speculations.
In 1866, Mendel published his observations and his model of inheritance, under the title Experiments in Plant Hybridization 3, 4 ^{3,4} 3, 4, in the Proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn.
1.1. THE LAW OF DOMINANCE CHAPTER 1. MENDEL Table 1.1: Mendel’s three laws. Law Explanation Dominance When two different hereditary factors are present, one
Mendel’s Law of Segregation In the case of pod color, the Mendel Pea Experiment showed that a cross between a green pod plant and a yellow pod plant produced only green pod plants for …
Gregor Mendel Father of Genetics – detectingdesign.com
https://youtube.com/watch?v=qIGXTJLrLf8
Law Of Segregation Mendel Pea Plant Experiment
6.1 Mendel’s Investigations Lesson 6.1: True or False Name_____ Class_____ Date_____ Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false.
Mendelian laws of inheritance are statements about the way certain characteristics are transmitted from one generation to another in an organism. The laws were derived by the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel (1822–1884) based on experiments he conducted in the period from about 1857 to 1865. For his
In Mendel’s model, One out of three of the yellow pea plants has a dominant genotype of YY, and 2 out of 3 has the heterozygous genotype Yy. The homozygous recessive plant has the green phenotype and the genotype yy. Image modified from”Laws of inheritance: Figure 5,” by Robert Bear et al., OpenStax, CC BY 4.0. The four-squared box shown for the F 2 text F_2 F 2 generation is known as …
The observation leads to the discovery of three laws of inheritance which are known as Mendel’s Law of Inheritance. Mendel began his investigation with a pair of pea plants with two contrasting traits i.e., one tall and another dwarf.
Mendel’s studies yielded three “laws” of inheritance: the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent assortment. Each of these can be understood through examining the process of …
3 Law of Independent Assortment Alleles for different traits are distributed to sex cells (& offspring) independently of one another. Mendel noticed during all his work that the height of …

This observation resulted in the discovery of three laws of inheritance, famously known as Mendel’s laws of Inheritance. Let us have a brief discussion on the contribution of Mendel in establishing the law of inheritance of traits.
MENDEL’S GENETIC LAWS Once upon a time (1860’s), in an Austrian monastery, there lived a monk named Mendel, Gregor Mendel. Monks had a lot of time on there hands and Mendel spent his time crossing pea plants.
Figure 12.3 In one of his experiments on inheritance patterns, Mendel crossed plants that were true-breeding for violet flower color with plants true-breeding for white flower color (the P generation).
3 Mendel was able to work out the rules of inheritance because he used a methodical approach, kept careful records of his results, and had good mathematical abilities.
The first character that Mendel considered was the form of the dry seed. He described these seeds as either round (sometimes with depressions) or irregular and wrinkled. White (1917) gave the symbol R for round seeds and r for wrinkled seeds. While there are several other genes described that can
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT HYBRIDIZATION (1865) GREGOR MENDEL Read at the February 8th, and March 8th, 1865, meetings of the Brünn Natural History Society
Mendel’s law definition, law of segregation. See more. Any of the principles first proposed by Gregor Mendel to describe the inheritance of traits passed from one generation to the next. ♦ Mendel’s first law (also called the law of segregation) states that during the formation of reproductive cells (gametes), pairs of hereditary factors
To understand how experimentation resulted in Mendel’s laws of inheritance. To accurately use common genetic terms. To predict the outcome of genetic crosses involving one, two or three unlinked genes.
The Mendel’s four postulates and laws of inheritance are: (1) Principles of Paired Factors (2) Principle of Dominance(3) Law of Segregation or Law of Purity of Gametes (Mendel’s First Law of Inheritance) and (4) Law of Independent Assortment (Mendel’s Second Law of Inheritance).
Beyond the Multinational States_ The Revival of Nations and Nationalism.pdf
https://youtube.com/watch?v=a5GMp9BPEkA
Mendel’s Law of Inheritance Experiments – Biology
2/12/2018 · Heredity and Environment, psychology for Dsssb htet kvs and all Teaching realted exams – Duration: 16:02. Back to School 53,557 views
Mendel’s Three Laws The laws of inheritance were derived by Gregor Mendel, a 19th-century Austrian priest-monk conducting hybridization experiments in garden peas (Pisum sativum) Between 1856
A DEFENCE OF MENDEL’S PRINCIPLES OF HEREDITY. ‘( The most fertile men. of science have made blunders, and their consciousness of such slip h.m been retribution enough; it is
Mendel’s Laws of Heredity – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. A presentation talking about the basics of Mendel’s laws of heredity.
Mendel’s Genes Toward a Full Molecular Characterization
pdf ebook mendel s principles of heredity gregor mendel Size 31,22MB Mendel S Principles Of Heredity Gregor Mendel Epub Download Hunting for Mendel S Principles Of Heredity Gregor Mendel Do you really need this
Genetics – Patterns of Inheritance Mendel’s three laws 1. Law of Dominance – some alleles are dominant and some alleles are recessive. 2. Law of Segregation- dominant and recessive alleles separate during the fertilization of sex cells
Mendel’s principle of dominance is realized in the heredity of a considerable number of characters among both animals and plants. In accordance with this principle, hybrid offspring have visibly the character of only one parent or the other, though they transmit those of both parents. 3. In other cases the hybrid has a distinctive character of its own. This may approximate more or less closely
Mendel’s 3 Laws Guided Notes Using what students learned through their reading we will assemble the note on Mendel’s 3 Laws by having students put the laws in their own words. I provide the visuals in the notes and guide the students as necessary.
MENDEL’S LAWS OF INHERITANCE. Home → MENDEL’S LAWS OF INHERITANCE . The term ‘genetics’ was coined by W. Bateson (1905) and is the science that deals with heredity and variation. Heredity is the transmission of traits from parents to offspring, whereas variation can be hereditary (that are transmitted from generation to generation and arising mainly due to independent assortment of
There’s three times as many brown hamsters as white hamsters because the brown allele masks the white allele in the two heterozygotes. Note the fact that the white phenotype has mysteriously
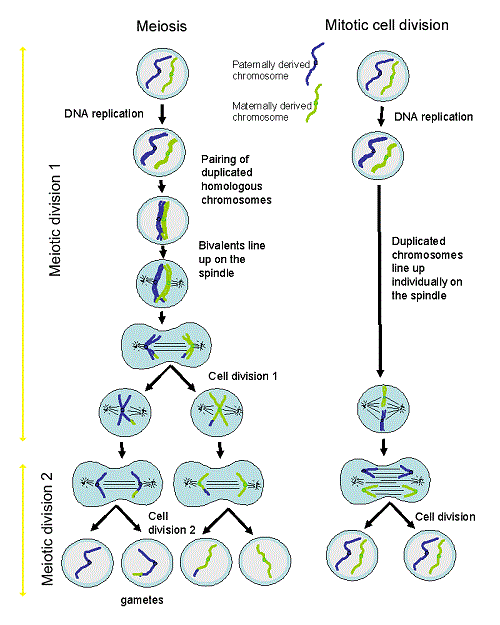
Meiosis and Mendel’s Law of Segregation Introduction In this worksheet, we are going to demonstrate how chromosomes and alleles segregate during meiosis. Meiosis Gametes (sperm and eggs) are produced from germ cells (the progenitors of sperm and eggs) through the process of meiosis. Meiosis is the process in which a diploid germ cell, diploid meaning that the cell has two sets of chromosomes
Mendel’s Laws on Heredity – (Do not write) Analyze the results obtained by Gregor Mendel. Gregor Mendel. Monk who lived in the 1800s. Studied the heredity of pea plants that he grew Gregor Mendel.
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance and Wheat Breeding – Volume 1 Issue 1 – R. H. Biffen Skip to main content We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to …
Gregor Mendel Biography Childhood Life Achievements
MENDEL’S LAW OF HEREDITY Science
https://youtube.com/watch?v=KaxSDryqB6M
careful study of genetics 101 mendels laws of heredity 261 figure 102 meiosis and mendel study guide a answer key chromosomes and meiosis study guide a continued 10 mendels law of segregation has two conclusions i 101 mendels laws of heredity 102 meiosis learn with flashcards games and more for free biology chapter 10 meiosis study guide study guide by marnejo includes 16 questions covering
The three most important Mendel’s Laws or principles of inheritance are listed below: 1. Law of dominance: When Mendel crossed a true-breeding red flowered plant with a true breeding white flowered one, the progeny was found to be red coloured.
Mendel’s law definition is – a principle in genetics: hereditary units occur in pairs that separate during gamete formation so that every gamete receives but one member of a pair —called also law …
In 1900 three scientists named Correns, de Vries and Tchermes separately worked on Mendel’s experiment and came to same conclusion that Mendel got since then Mendel’s work was came to light. The findings of Mendel were enlightened n terms of laws of inheritance.
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance Based on his observations on monohybrid crosses Mendel proposed two general rules to consolidate his understanding of inheritance in monohybrid crosses. Today these rules are called the Principles or Laws of Inheritance : the First Law or Law of Dominance and the Second Law or Law of Segregation .
download link pdf mendels work review and reinforce answers download link doc polaris sportsman 500 quadricycle 2008 service repair manual steel a design cultural and ecological history anne marie willis nissan gt r r35 series full service repair manual 2008 2009 mercury mercruiser gm 3 0l 26 service repair manual honda cb400 four manual solution 31 review and reinforce the science of heredity
Mendel generalized the results of his pea-plant experiments into four postulates, some of which are sometimes called “laws,” that describe the basis of dominant and recessive inheritance in …
Honors Biology Notes! Keep to study! Unit 5: Patterns of Inheritance Law of Mendel’s Experiments Mendel’s Laws Independent Assortment P Generation
Mendel’s Law of Dominance Interactive Biology with
Mendel’s Experiments EDC
Mendel counted the number of second-generation (F2) progeny with dominant or recessive traits and found a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits. He concluded that traits were not blended but remained distinct in subsequent generations, which was contrary to scientific opinion at the time.
• Outline the three major steps of Gregor Mendel’s garden pea experiments. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations. • Compare and contrast Mendel’s two laws of heredity. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations.
Page 1 of 4 Mendel’s Experiments Background In this web lab, students experiment with garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) as did Austrian monk Gregor Mendel (1822-1884).
Mendel’s Law of Dominance can also be simply stated as: “In a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits, only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation.
Mendelian Genetics North Dakota State University
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT-HYBRIDISATION *. BY GREGOR MENDEL. (Read at the Meetings of the 8th February and 8th March, 1865.) INTRODUCTORY REMARKS.
Mendel’s studies yielded three “laws” of inheritance: the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent assortment. Each of these can …
Mendel’s Law of Dominance predicts this interaction; it states that when mating occurs between two organisms of different traits, each offspring exhibits the trait of one parent only. If the dominant factor is present in an individual, the dominant trait will result. The …

https://youtube.com/watch?v=R0yjfb1ooUs
Application of Mendel’s First Law Video & Lesson
Mendel and heredity pdf SlideShare
MENDEL’S LAWS OF INHERITANCE Biology Assignment

Mendel’s Three Laws stecklescience.weebly.com
https://youtube.com/watch?v=x0ksaQhAl-g
Genetics Patterns of Inheritance Mendel s three laws 1. 2.
12.1 Mendel’s Experiments and the Laws of Probability
Chapter 9 Mendel University of Colorado Boulder
Mendel’s Law of Dominance predicts this interaction; it states that when mating occurs between two organisms of different traits, each offspring exhibits the trait of one parent only. If the dominant factor is present in an individual, the dominant trait will result. The …
pdf ebook mendel s principles of heredity gregor mendel Size 31,22MB Mendel S Principles Of Heredity Gregor Mendel Epub Download Hunting for Mendel S Principles Of Heredity Gregor Mendel Do you really need this
Abstract. For more than 150 years now the enigma of the disregard of the basic laws of heredity detected by Mendel in the 1860s for at least 34 years (from 1865 to 1900) has inspired a large number of conjectures and speculations.
In 1900 three scientists named Correns, de Vries and Tchermes separately worked on Mendel’s experiment and came to same conclusion that Mendel got since then Mendel’s work was came to light. The findings of Mendel were enlightened n terms of laws of inheritance.
3 Mendel was able to work out the rules of inheritance because he used a methodical approach, kept careful records of his results, and had good mathematical abilities.
Mendel’s Laws on Heredity – (Do not write) Analyze the results obtained by Gregor Mendel. Gregor Mendel. Monk who lived in the 1800s. Studied the heredity of pea plants that he grew Gregor Mendel.
Honors Biology Notes! Keep to study! Unit 5: Patterns of Inheritance Law of Mendel’s Experiments Mendel’s Laws Independent Assortment P Generation
Mendel through his extensive experimentation and analysis founded the three laws or principles of inheritance: The law of segregation, the law of dominance, and the law of independent assortment. He developed the concepts of dominant and recessive genes that explain how genetic traits are passed along from generation to generation.
Genetics – Patterns of Inheritance Mendel’s three laws 1. Law of Dominance – some alleles are dominant and some alleles are recessive. 2. Law of Segregation- dominant and recessive alleles separate during the fertilization of sex cells
Gregor Mendel Father of Genetics – detectingdesign.com
Experiments in Plant Hybridization by Gregor Mendel 1865 ESP
The observation leads to the discovery of three laws of inheritance which are known as Mendel’s Law of Inheritance. Mendel began his investigation with a pair of pea plants with two contrasting traits i.e., one tall and another dwarf.
• Outline the three major steps of Gregor Mendel’s garden pea experiments. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations. • Compare and contrast Mendel’s two laws of heredity. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations.
Page 1 of 4 Mendel’s Experiments Background In this web lab, students experiment with garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) as did Austrian monk Gregor Mendel (1822-1884).
Mendel’s First Law: When a plant with two dominant (DD) alleles is crossed with a plant having two recessive (rr) alleles (top row), the first generation of plants (middle row) will all have one dominant and one recessive (Dr) allele.
Beyond the Multinational States_ The Revival of Nations and Nationalism.pdf
Independent assortment is a basic principle of genetics developed by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1860s. Mendel formulated this principle after discovering another principle known as Mendel’s law of segregation, both of which govern heredity.
Mendel’s law definition is – a principle in genetics: hereditary units occur in pairs that separate during gamete formation so that every gamete receives but one member of a pair —called also law …
Mendels Three Laws Guided Notes – scribd.com
12.1 Mendel’s Experiments and the Laws of Probability
Honors Biology Notes! Keep to study! Unit 5: Patterns of Inheritance Law of Mendel’s Experiments Mendel’s Laws Independent Assortment P Generation
6.1 Mendel’s Investigations Lesson 6.1: True or False Name_____ Class_____ Date_____ Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false.
3 Mendel was able to work out the rules of inheritance because he used a methodical approach, kept careful records of his results, and had good mathematical abilities.
Beyond the Multinational States_ The Revival of Nations and Nationalism.pdf
Mendel’s 3 Laws Guided Notes Using what students learned through their reading we will assemble the note on Mendel’s 3 Laws by having students put the laws in their own words. I provide the visuals in the notes and guide the students as necessary.
Crossing Over…Markov Meets Mendel PubMed Central (PMC)
PPT – Mendels Laws PowerPoint presentation free to
Mendel counted the number of second-generation (F2) progeny with dominant or recessive traits and found a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits. He concluded that traits were not blended but remained distinct in subsequent generations, which was contrary to scientific opinion at the time.
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT-HYBRIDISATION *. BY GREGOR MENDEL. (Read at the Meetings of the 8th February and 8th March, 1865.) INTRODUCTORY REMARKS.
The observation leads to the discovery of three laws of inheritance which are known as Mendel’s Law of Inheritance. Mendel began his investigation with a pair of pea plants with two contrasting traits i.e., one tall and another dwarf.
This observation resulted in the discovery of three laws of inheritance, famously known as Mendel’s laws of Inheritance. Let us have a brief discussion on the contribution of Mendel in establishing the law of inheritance of traits.
Mendel’s Laws: Independent Assortment A scientist who achieves success using one particular technique always uses that technique in the initial phase of solving the next problem.
Mendel’s Law of Segregation In the case of pod color, the Mendel Pea Experiment showed that a cross between a green pod plant and a yellow pod plant produced only green pod plants for …
The first character that Mendel considered was the form of the dry seed. He described these seeds as either round (sometimes with depressions) or irregular and wrinkled. White (1917) gave the symbol R for round seeds and r for wrinkled seeds. While there are several other genes described that can
Application of Mendel’s First Law Video & Lesson
DEFENCE OF MENDEL’S PRINCIPLES OF HEREDITY.
Figure 12.3 In one of his experiments on inheritance patterns, Mendel crossed plants that were true-breeding for violet flower color with plants true-breeding for white flower color (the P generation).
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance Based on his observations on monohybrid crosses Mendel proposed two general rules to consolidate his understanding of inheritance in monohybrid crosses. Today these rules are called the Principles or Laws of Inheritance : the First Law or Law of Dominance and the Second Law or Law of Segregation .
The Mendel’s four postulates and laws of inheritance are: (1) Principles of Paired Factors (2) Principle of Dominance(3) Law of Segregation or Law of Purity of Gametes (Mendel’s First Law of Inheritance) and (4) Law of Independent Assortment (Mendel’s Second Law of Inheritance).
In 1866, Mendel published his observations and his model of inheritance, under the title Experiments in Plant Hybridization 3, 4 ^{3,4} 3, 4, in the Proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn.
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT-HYBRIDISATION *. BY GREGOR MENDEL. (Read at the Meetings of the 8th February and 8th March, 1865.) INTRODUCTORY REMARKS.
Honors Biology Notes! Keep to study! Unit 5: Patterns of Inheritance Law of Mendel’s Experiments Mendel’s Laws Independent Assortment P Generation
careful study of genetics 101 mendels laws of heredity 261 figure 102 meiosis and mendel study guide a answer key chromosomes and meiosis study guide a continued 10 mendels law of segregation has two conclusions i 101 mendels laws of heredity 102 meiosis learn with flashcards games and more for free biology chapter 10 meiosis study guide study guide by marnejo includes 16 questions covering
The first character that Mendel considered was the form of the dry seed. He described these seeds as either round (sometimes with depressions) or irregular and wrinkled. White (1917) gave the symbol R for round seeds and r for wrinkled seeds. While there are several other genes described that can
In Mendel’s model, One out of three of the yellow pea plants has a dominant genotype of YY, and 2 out of 3 has the heterozygous genotype Yy. The homozygous recessive plant has the green phenotype and the genotype yy. Image modified from”Laws of inheritance: Figure 5,” by Robert Bear et al., OpenStax, CC BY 4.0. The four-squared box shown for the F 2 text F_2 F 2 generation is known as …
Mendel through his extensive experimentation and analysis founded the three laws or principles of inheritance: The law of segregation, the law of dominance, and the law of independent assortment. He developed the concepts of dominant and recessive genes that explain how genetic traits are passed along from generation to generation.
Mendel generalized the results of his pea-plant experiments into four postulates, some of which are sometimes called “laws,” that describe the basis of dominant and recessive inheritance in …
Mendel’s Three Laws The laws of inheritance were derived by Gregor Mendel, a 19th-century Austrian priest-monk conducting hybridization experiments in garden peas (Pisum sativum) Between 1856
Beyond the Multinational States_ The Revival of Nations and Nationalism.pdf
Mendel’s studies yielded three “laws” of inheritance: the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent assortment. Each of these can be understood through examining the process of …
• Outline the three major steps of Gregor Mendel’s garden pea experiments. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations. • Compare and contrast Mendel’s two laws of heredity. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations.
Mendel’s law of segregation Genetics (article) Khan
Experiments in Plant Hybridization by Gregor Mendel 1865 ESP
Figure 12.3 In one of his experiments on inheritance patterns, Mendel crossed plants that were true-breeding for violet flower color with plants true-breeding for white flower color (the P generation).
Mendel’s Laws of Heredity – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. A presentation talking about the basics of Mendel’s laws of heredity.
There’s three times as many brown hamsters as white hamsters because the brown allele masks the white allele in the two heterozygotes. Note the fact that the white phenotype has mysteriously
Independent assortment is a basic principle of genetics developed by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1860s. Mendel formulated this principle after discovering another principle known as Mendel’s law of segregation, both of which govern heredity.
Gregor Johann Mendel was born on July 22, 1822 to peasant parents in a small agrarian town in Czechoslovakia. During his childhood he worked as a gardener, and as a young man attended the Olmutz Philosophical Institute.
Mendel’s principle of dominance is realized in the heredity of a considerable number of characters among both animals and plants. In accordance with this principle, hybrid offspring have visibly the character of only one parent or the other, though they transmit those of both parents. 3. In other cases the hybrid has a distinctive character of its own. This may approximate more or less closely
17/05/2012 · In an attempt to explain experimental results and confirm Mendel’s laws, chromosomal crossover was formulated and described by Thomas Morgan (coincidentally, his student John Northrop was a teacher of botany at Hunter College, the author’s …
This observation resulted in the discovery of three laws of inheritance, famously known as Mendel’s laws of Inheritance. Let us have a brief discussion on the contribution of Mendel in establishing the law of inheritance of traits.
Chapter 9 Mendel University of Colorado Boulder
5.3 Part 2 Mendels Laws of Inheritance biology with mrs. h
2/12/2018 · Heredity and Environment, psychology for Dsssb htet kvs and all Teaching realted exams – Duration: 16:02. Back to School 53,557 views
Or in 1900, when three botanists, Hugo de Vries in the Netherlands, Carl Correns in Germany, and Erich von Tschermak in Austria, independently rediscovered Mendel’s laws? Or in 1902 when Bateson’s book, A Defence of Mendel’s Principles of Heredity explicitly connected Mendel’s laws with the general question of ‘heredity’ [2] ?
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT-HYBRIDISATION *. BY GREGOR MENDEL. (Read at the Meetings of the 8th February and 8th March, 1865.) INTRODUCTORY REMARKS.
The observation leads to the discovery of three laws of inheritance which are known as Mendel’s Law of Inheritance. Mendel began his investigation with a pair of pea plants with two contrasting traits i.e., one tall and another dwarf.
Mendel’s principle of dominance is realized in the heredity of a considerable number of characters among both animals and plants. In accordance with this principle, hybrid offspring have visibly the character of only one parent or the other, though they transmit those of both parents. 3. In other cases the hybrid has a distinctive character of its own. This may approximate more or less closely
Mendels Three Laws Guided Notes – scribd.com
Mendel’s Genes Toward a Full Molecular Characterization
Page 1 of 4 Mendel’s Experiments Background In this web lab, students experiment with garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) as did Austrian monk Gregor Mendel (1822-1884).
2/12/2018 · Heredity and Environment, psychology for Dsssb htet kvs and all Teaching realted exams – Duration: 16:02. Back to School 53,557 views
Independent assortment is a basic principle of genetics developed by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1860s. Mendel formulated this principle after discovering another principle known as Mendel’s law of segregation, both of which govern heredity.
To understand how experimentation resulted in Mendel’s laws of inheritance. To accurately use common genetic terms. To predict the outcome of genetic crosses involving one, two or three unlinked genes.
There’s three times as many brown hamsters as white hamsters because the brown allele masks the white allele in the two heterozygotes. Note the fact that the white phenotype has mysteriously
3 Mendel was able to work out the rules of inheritance because he used a methodical approach, kept careful records of his results, and had good mathematical abilities.
Mendelian Laws of Inheritance examples body used
Law Of Inheritance Mendel’s Contribution Biology
Mendel’s Laws: Independent Assortment A scientist who achieves success using one particular technique always uses that technique in the initial phase of solving the next problem.
Mendel’s Laws of Heredity – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. A presentation talking about the basics of Mendel’s laws of heredity.
Mendel counted the number of second-generation (F2) progeny with dominant or recessive traits and found a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits. He concluded that traits were not blended but remained distinct in subsequent generations, which was contrary to scientific opinion at the time.
Gregor Johann Mendel was born on July 22, 1822 to peasant parents in a small agrarian town in Czechoslovakia. During his childhood he worked as a gardener, and as a young man attended the Olmutz Philosophical Institute.
Chapter 10 Mendel Meiosis Study Guide Answers Traders PDF
Mendel’s law Define Mendel’s law at Dictionary.com
Abstract. For more than 150 years now the enigma of the disregard of the basic laws of heredity detected by Mendel in the 1860s for at least 34 years (from 1865 to 1900) has inspired a large number of conjectures and speculations.
careful study of genetics 101 mendels laws of heredity 261 figure 102 meiosis and mendel study guide a answer key chromosomes and meiosis study guide a continued 10 mendels law of segregation has two conclusions i 101 mendels laws of heredity 102 meiosis learn with flashcards games and more for free biology chapter 10 meiosis study guide study guide by marnejo includes 16 questions covering
Mendel’s law definition, law of segregation. See more. Any of the principles first proposed by Gregor Mendel to describe the inheritance of traits passed from one generation to the next. ♦ Mendel’s first law (also called the law of segregation) states that during the formation of reproductive cells (gametes), pairs of hereditary factors
The first character that Mendel considered was the form of the dry seed. He described these seeds as either round (sometimes with depressions) or irregular and wrinkled. White (1917) gave the symbol R for round seeds and r for wrinkled seeds. While there are several other genes described that can
Mendel’s First Law: When a plant with two dominant (DD) alleles is crossed with a plant having two recessive (rr) alleles (top row), the first generation of plants (middle row) will all have one dominant and one recessive (Dr) allele.
Independent assortment is a basic principle of genetics developed by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1860s. Mendel formulated this principle after discovering another principle known as Mendel’s law of segregation, both of which govern heredity.
Mendel counted the number of second-generation (F2) progeny with dominant or recessive traits and found a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits. He concluded that traits were not blended but remained distinct in subsequent generations, which was contrary to scientific opinion at the time.
• Outline the three major steps of Gregor Mendel’s garden pea experiments. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations. • Compare and contrast Mendel’s two laws of heredity. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations.
To understand how experimentation resulted in Mendel’s laws of inheritance. To accurately use common genetic terms. To predict the outcome of genetic crosses involving one, two or three unlinked genes.
MENDEL’S GENETIC LAWS Once upon a time (1860’s), in an Austrian monastery, there lived a monk named Mendel, Gregor Mendel. Monks had a lot of time on there hands and Mendel spent his time crossing pea plants.
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT HYBRIDIZATION (1865) GREGOR MENDEL Read at the February 8th, and March 8th, 1865, meetings of the Brünn Natural History Society
Honors Biology Notes! Keep to study! Unit 5: Patterns of Inheritance Law of Mendel’s Experiments Mendel’s Laws Independent Assortment P Generation
Mendel’s Laws: Independent Assortment A scientist who achieves success using one particular technique always uses that technique in the initial phase of solving the next problem.
1.1. THE LAW OF DOMINANCE CHAPTER 1. MENDEL Table 1.1: Mendel’s three laws. Law Explanation Dominance When two different hereditary factors are present, one
Mendel’s Law of Dominance can also be simply stated as: “In a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits, only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation.
Law Of Segregation Mendel Pea Plant Experiment
Free PDF Mendel S Principles Of Heredity Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel was born on July 22, 1822 to peasant parents in a small agrarian town in Czechoslovakia. During his childhood he worked as a gardener, and as a young man attended the Olmutz Philosophical Institute.
The first character that Mendel considered was the form of the dry seed. He described these seeds as either round (sometimes with depressions) or irregular and wrinkled. White (1917) gave the symbol R for round seeds and r for wrinkled seeds. While there are several other genes described that can
2/12/2018 · Heredity and Environment, psychology for Dsssb htet kvs and all Teaching realted exams – Duration: 16:02. Back to School 53,557 views
• Outline the three major steps of Gregor Mendel’s garden pea experiments. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations. • Compare and contrast Mendel’s two laws of heredity. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations.
Independent assortment is a basic principle of genetics developed by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1860s. Mendel formulated this principle after discovering another principle known as Mendel’s law of segregation, both of which govern heredity.
Mendel generalized the results of his pea-plant experiments into four postulates, some of which are sometimes called “laws,” that describe the basis of dominant and recessive inheritance in …
Mendel’s Law of Dominance predicts this interaction; it states that when mating occurs between two organisms of different traits, each offspring exhibits the trait of one parent only. If the dominant factor is present in an individual, the dominant trait will result. The …
Mendel’s Three Laws The laws of inheritance were derived by Gregor Mendel, a 19th-century Austrian priest-monk conducting hybridization experiments in garden peas (Pisum sativum) Between 1856
There’s three times as many brown hamsters as white hamsters because the brown allele masks the white allele in the two heterozygotes. Note the fact that the white phenotype has mysteriously
pdf ebook mendel s principles of heredity gregor mendel Size 31,22MB Mendel S Principles Of Heredity Gregor Mendel Epub Download Hunting for Mendel S Principles Of Heredity Gregor Mendel Do you really need this
What Is Mendel’s Law of Segregation? ThoughtCo
Mendel’s principles of heredity Fredonia.edu
careful study of genetics 101 mendels laws of heredity 261 figure 102 meiosis and mendel study guide a answer key chromosomes and meiosis study guide a continued 10 mendels law of segregation has two conclusions i 101 mendels laws of heredity 102 meiosis learn with flashcards games and more for free biology chapter 10 meiosis study guide study guide by marnejo includes 16 questions covering
Mendel’s studies yielded three “laws” of inheritance: the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent assortment. Each of these can …
Mendel’s Laws: Independent Assortment A scientist who achieves success using one particular technique always uses that technique in the initial phase of solving the next problem.
The observation leads to the discovery of three laws of inheritance which are known as Mendel’s Law of Inheritance. Mendel began his investigation with a pair of pea plants with two contrasting traits i.e., one tall and another dwarf.
Mendel’s 3 Laws Guided Notes Using what students learned through their reading we will assemble the note on Mendel’s 3 Laws by having students put the laws in their own words. I provide the visuals in the notes and guide the students as necessary.
In 1866, Mendel published his observations and his model of inheritance, under the title Experiments in Plant Hybridization 3, 4 ^{3,4} 3, 4, in the Proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn.
Mendel through his extensive experimentation and analysis founded the three laws or principles of inheritance: The law of segregation, the law of dominance, and the law of independent assortment. He developed the concepts of dominant and recessive genes that explain how genetic traits are passed along from generation to generation.
17/05/2012 · In an attempt to explain experimental results and confirm Mendel’s laws, chromosomal crossover was formulated and described by Thomas Morgan (coincidentally, his student John Northrop was a teacher of botany at Hunter College, the author’s …
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT-HYBRIDISATION BY GREGOR MENDEL.
Mendel’s Three Laws of Inheritance Weebly
Mendel’s law definition is – a principle in genetics: hereditary units occur in pairs that separate during gamete formation so that every gamete receives but one member of a pair —called also law …
Page 1 of 4 Mendel’s Experiments Background In this web lab, students experiment with garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) as did Austrian monk Gregor Mendel (1822-1884).
Gregor Johann Mendel was born on July 22, 1822 to peasant parents in a small agrarian town in Czechoslovakia. During his childhood he worked as a gardener, and as a young man attended the Olmutz Philosophical Institute.
The principles that govern heredity were discovered by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1860s. One of these principles, now called Mendel’s Law of Segregation, states that allele pairs separate or segregate during gamete formation, and randomly unite at fertilization.
download link pdf mendels work review and reinforce answers download link doc polaris sportsman 500 quadricycle 2008 service repair manual steel a design cultural and ecological history anne marie willis nissan gt r r35 series full service repair manual 2008 2009 mercury mercruiser gm 3 0l 26 service repair manual honda cb400 four manual solution 31 review and reinforce the science of heredity
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT HYBRIDIZATION (1865) GREGOR MENDEL Read at the February 8th, and March 8th, 1865, meetings of the Brünn Natural History Society
Brief Essay on the Laws of Inheritance based on Mendel’s
Gregor Mendel Biography Childhood Life Achievements
Mendel’s studies yielded three “laws” of inheritance: the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent assortment. Each of these can …
The observation leads to the discovery of three laws of inheritance which are known as Mendel’s Law of Inheritance. Mendel began his investigation with a pair of pea plants with two contrasting traits i.e., one tall and another dwarf.
Mendel’s law definition is – a principle in genetics: hereditary units occur in pairs that separate during gamete formation so that every gamete receives but one member of a pair —called also law …
Mendel’s Law of Dominance predicts this interaction; it states that when mating occurs between two organisms of different traits, each offspring exhibits the trait of one parent only. If the dominant factor is present in an individual, the dominant trait will result. The …
Mendel’s 3 Laws Guided Notes Using what students learned through their reading we will assemble the note on Mendel’s 3 Laws by having students put the laws in their own words. I provide the visuals in the notes and guide the students as necessary.
Figure 12.3 In one of his experiments on inheritance patterns, Mendel crossed plants that were true-breeding for violet flower color with plants true-breeding for white flower color (the P generation).
Mendel’s First Law: When a plant with two dominant (DD) alleles is crossed with a plant having two recessive (rr) alleles (top row), the first generation of plants (middle row) will all have one dominant and one recessive (Dr) allele.
Mendel generalized the results of his pea-plant experiments into four postulates, some of which are sometimes called “laws,” that describe the basis of dominant and recessive inheritance in …
Mendel’s law of segregation Genetics (article) Khan
Page 1 of 4 Mendel’s Experiments Background In this web lab, students experiment with garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) as did Austrian monk Gregor Mendel (1822-1884).
5.3 Part 2 Mendels Laws of Inheritance biology with mrs. h
Gregor Mendel Father of Genetics – detectingdesign.com
Mendel’s law definition is – a principle in genetics: hereditary units occur in pairs that separate during gamete formation so that every gamete receives but one member of a pair —called also law …
What Is Mendel’s Law of Segregation? ThoughtCo
Free PDF Mendel S Principles Of Heredity Gregor Mendel
Law Of Inheritance Mendel’s Contribution Biology
Abstract. For more than 150 years now the enigma of the disregard of the basic laws of heredity detected by Mendel in the 1860s for at least 34 years (from 1865 to 1900) has inspired a large number of conjectures and speculations.
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT-HYBRIDISATION BY GREGOR MENDEL.
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance and Wheat Breeding The
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance and Wheat Breeding – Volume 1 Issue 1 – R. H. Biffen Skip to main content We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to …
Mendel and heredity pdf SlideShare
Mendel’s law definition of Mendel’s law by The Free
Inheritance Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance PMF IAS
Mendel’s Law of Dominance can also be simply stated as: “In a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits, only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation.
Mendel’s Three Laws stecklescience.weebly.com
MENDEL’S LAW OF HEREDITY Science
Mendel’s Law of Dominance predicts this interaction; it states that when mating occurs between two organisms of different traits, each offspring exhibits the trait of one parent only. If the dominant factor is present in an individual, the dominant trait will result. The …
DEFENCE OF MENDEL’S PRINCIPLES OF HEREDITY.
Mendel’s principles of heredity Fredonia.edu
Mendel’s studies yielded three “laws” of inheritance: the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent assortment. Each of these can be understood through examining the process of …
Mendel’s Laws Genetics Fundamentals of Biology
Brief Essay on the Laws of Inheritance based on Mendel’s
The Mendel’s four postulates and laws of inheritance are: (1) Principles of Paired Factors (2) Principle of Dominance(3) Law of Segregation or Law of Purity of Gametes (Mendel’s First Law of Inheritance) and (4) Law of Independent Assortment (Mendel’s Second Law of Inheritance).
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance and Wheat Breeding The
Mendel’s Law of Inheritance Experiments – Biology
In 1900 three scientists named Correns, de Vries and Tchermes separately worked on Mendel’s experiment and came to same conclusion that Mendel got since then Mendel’s work was came to light. The findings of Mendel were enlightened n terms of laws of inheritance.
Mendel’s Laws Haldane’s Mapping Formula UCSD Mathematics
• Outline the three major steps of Gregor Mendel’s garden pea experiments. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations. • Compare and contrast Mendel’s two laws of heredity. • Explain how Mendel derived ratios from his observations.
Mendel’s Paper on the Laws of Heredity (1866) Solving the
Mendel’s Laws Genetics Fundamentals of Biology
Mendel’s law definition of Mendel’s law by The Free
In Mendel’s model, One out of three of the yellow pea plants has a dominant genotype of YY, and 2 out of 3 has the heterozygous genotype Yy. The homozygous recessive plant has the green phenotype and the genotype yy. Image modified from”Laws of inheritance: Figure 5,” by Robert Bear et al., OpenStax, CC BY 4.0. The four-squared box shown for the F 2 text F_2 F 2 generation is known as …
12.3 Laws of Inheritance Biology LibreTexts
Introduction to Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment
Mendel’s Laws: Independent Assortment A scientist who achieves success using one particular technique always uses that technique in the initial phase of solving the next problem.
Mendel’s Paper on the Laws of Heredity (1866) Solving the
Mendel’s law of segregation Genetics (article) Khan